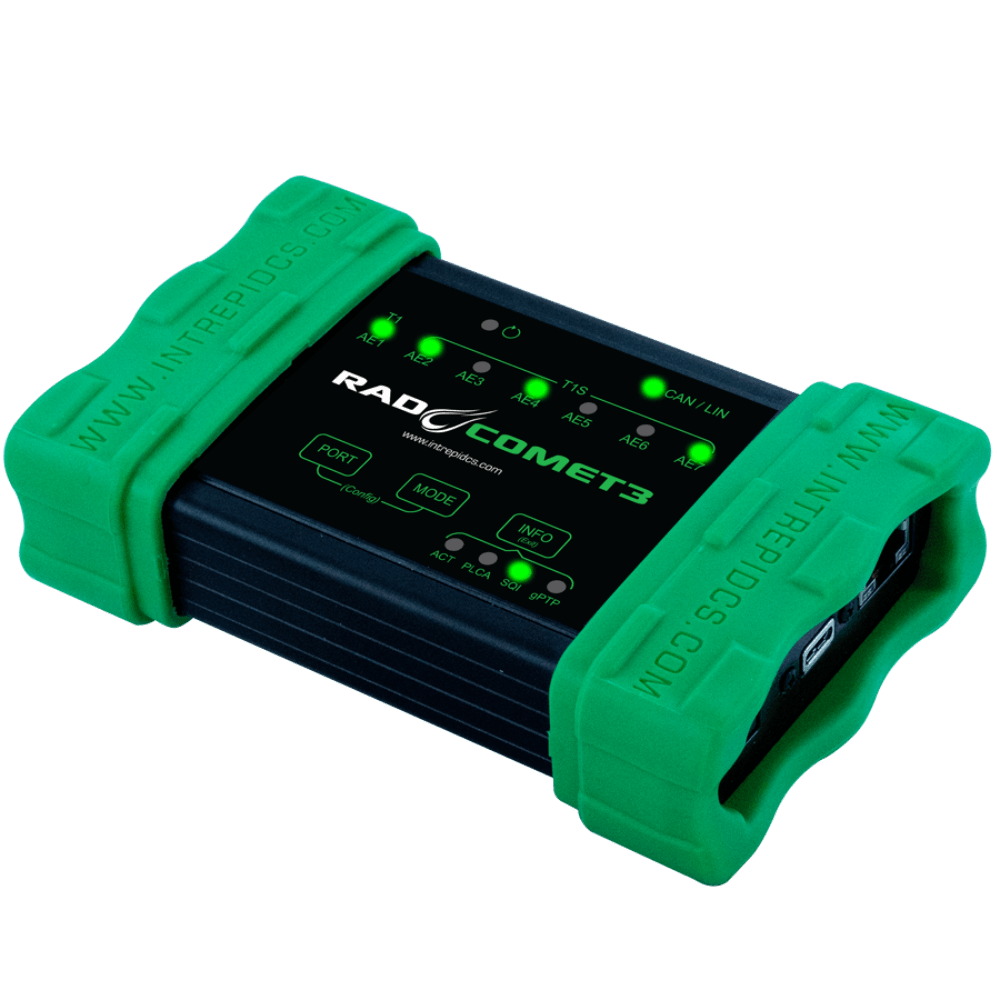
RAD-Comet 3
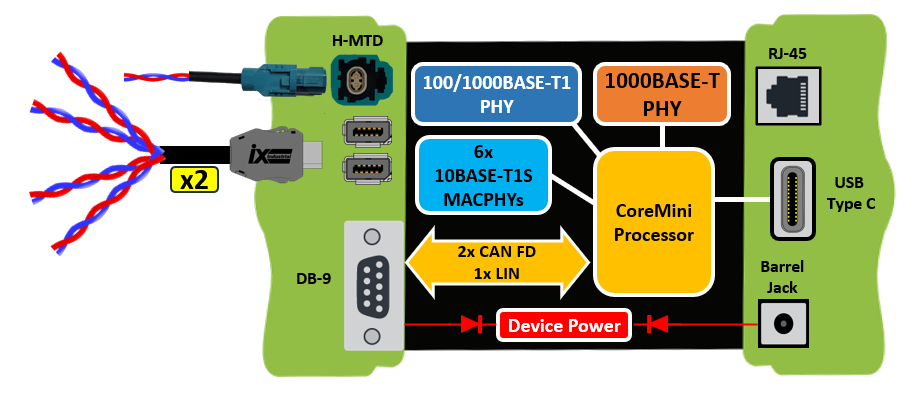
6x 10BASE-T1S Development Interface with 100/1000BASE-T1, 1000BASE-T, CAN FD and LIN6x 10BASE-T1S Development Interface with 100/1000BASE-T1, 1000BASE-T, CAN FD and LIN
The RAD-Comet 3 is a versatile device for developing and testing 10BASE-T1S communication in automotive systems. It can be programmed to simulate a node on a 10BASE-T1S network as well as capture and analyze 10BASE-T1S traffic simultaneously with other vehicle networks. All Ethernet, CAN, and LIN traffic are time-stamped precisely for logging or analysis in Vehicle Spy software.
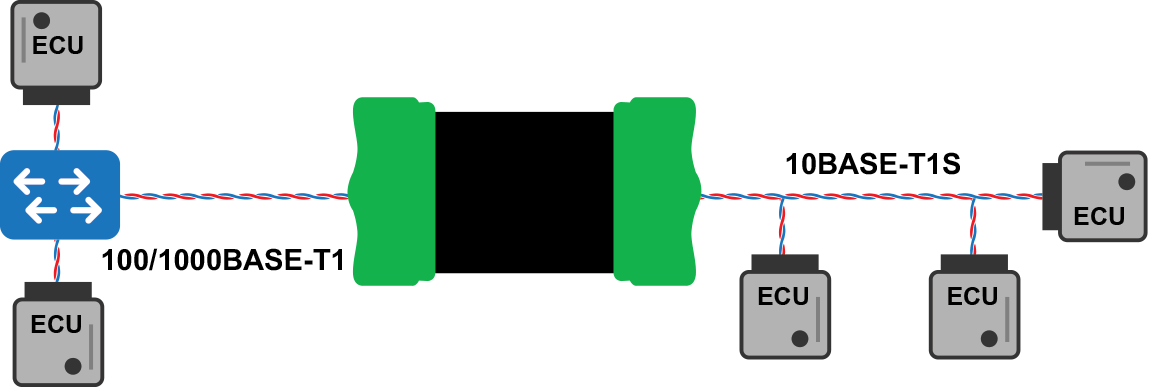
When configured as a media converter, the RAD Comet 3 can bridge between any of its 3 Ethernet physical layers. This is useful for connecting a PC to an Automotive Ethernet device for observing network activity in Wireshark or Vehicle Spy. It is also useful for integrating a 10BASE-T1S device or network into a 100/1000BASE-T1.
Primary Use Cases
- Network Monitoring and Diagnostics
- Media Converter for 10BASE-T1S and 100/1000BASE-T1
- Gateway applications between Ethernet, CAN FD and LIN
- ECU Simulation and Testing
Product Features
- Time Synchronization
- gPTP Time Synchronization using 100BASE-T1 or 100/1000BASE-T
- Intrepid Time Sync (ITS) with other Intrepid products
- OPEN Alliance TC10 Sleep and Wakeup (100/1000BASE-T1)
- MACsec Authentication/Encryption Support (100/1000BASE-T1)
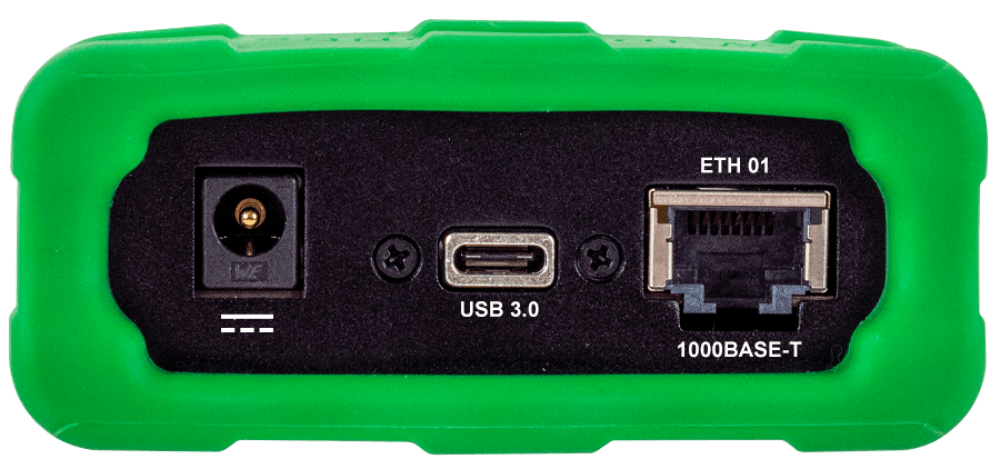
- Device power via DB9
- Protected DC power interface suitable for vehicle integration
- Status LEDs
- Network status and activity
- T1 and T1S SQI indication
- T1S PLCA Status
- PC Connectivity
- Data connection via USB 3 or Gigabit Ethernet (1000BASE-T)
- Compatibility with Vehicle Spy and Wireshark
- Open-Source Intrepid API for direct network access in Windows or Linux applications.
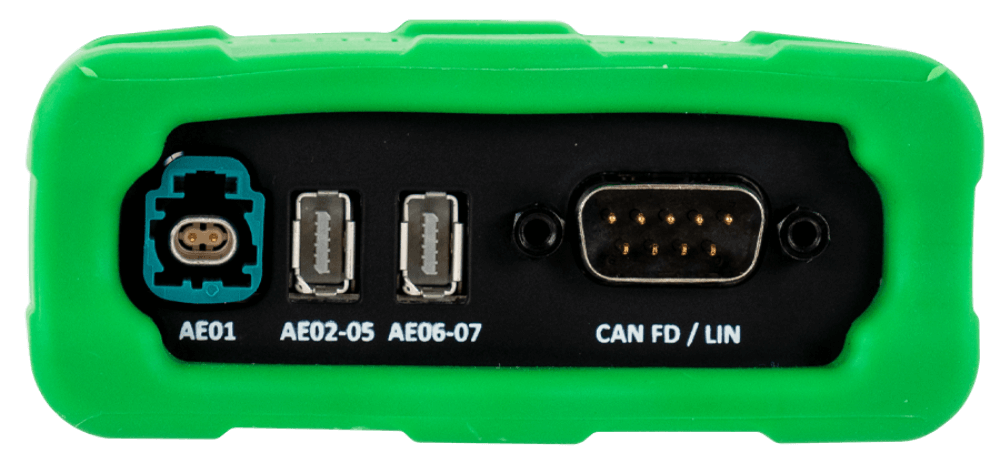
Network Interfaces
- 6x 10BASE-T1S (AD330X)
- 1x 100/1000BASE-T1 (88Q2221M)
- 1x 10/100/1000BASE-T
- 2x ISO CAN FD channels with selectable on-board termination
- 1x LIN
Operational Overview and Use Cases
Media Conversion
The RAD-Comet 3 can be used as a media converter between 10BASE-T1S and either of the other Ethernet physical layers available on the device.
10BASE-T1S ⇔ 10/100/1000BASE-T
10BASE-T1S ⇔ 100/1000BASE-T1
It can also serve as a media converter for 100/1000BASE-T1
100/1000BASE-T ⇔ 100/1000BASE-T1 Media Conversion
Stand-Alone Gateway
Elaborate gateways can be implemented between any of the networks available on the RAD-Comet 3.
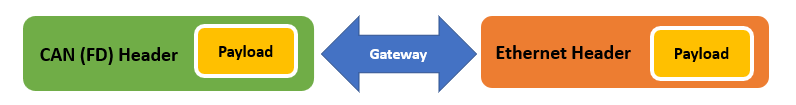
CAN/Ethernet Gateway
Payloads can be extracted from frames arriving on one network, placed into a different PDU structure with a different header and sent to another network.
Examples of this utility include (but not limited to):
- Networking devices from different architectures for a proof-of-concept
- Networking devices during the transition from one vehicle architecture to the next
- Streaming select (or all) network traffic for logging and analysis
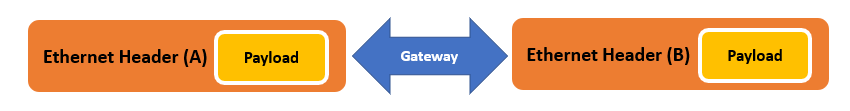
Ethernet/Ethernet Gateway
Frames can arrive on one Ethernet network and sent out to another network directly, or after changing anything in the header or payload.
This functionality can be used to realize many novel functions useful in vehicle testing.
For Example:
- Changing frame destination
- MAC Spoofing
- Layer 3/4 Address Translation
- Payload scaling
- Payload manipulation (Boundary testing, fault injection, penetration testing, etc.)
Simulation and Scripting
Using Vehicle Spy you can define transmit messages on any network with custom data and send them manually or on a schedule of your choosing. You can also write intelligent scripts that implement arbitrary logic and compile them into embedded scripts which can run within the device itself. This functionality allows you to create specialized test scenarios, and to simulate ECUs and gateways.
PHY Register access
In any mode, each PHY can be accessed by the embedded processor over MDIO in order to read and write configuration registers.
10BASE-T1S Comparison Chart
| Key Features | RAD-Comet 3 | RAD-Comet 2 | RAD-Meteor |
| 10BASE-T1S | 6x Analog Devices AD330X PHY | 2x Microchip LAN8671 PHY | 1x Microchip LAN867X PHY |
| 100/1000BASE-T1 | 1x 88Q2221M PHY | Marvell 88Q2221M PHY | 0 |
| CAN FD | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| LIN | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Connector | ix Industrial™ for T1S and H-MTD for T1 | ix Industrial™ for T1S and H-MTD for T1 | Terminal Block |
| Voltage Input | 5.5-40V | 5.5-40V | 125mA at 5 V (bus load 1%), 140 mA at 5V (Test Mode 1) |
| Power | Barrel Jack | Barrel Jack | USB Type C |
| Configure | Isolated USB 3.1 connection or Gigabit Ethernet (1000BASE-T) | Isolated USB 3.1 connection or Gigabit Ethernet (1000BASE-T) | USB Type-C |
| TC10 | Yes (100/1000BASE-T1) | Yes (100/1000BASE-T1) | No |
| gPTP | Yes (100/1000BASE-T1) | Yes (100/1000BASE-T1) | No |
| MACsec | Yes (100/1000BASE-T1) | Yes (100/1000BASE-T1) | No |
| Programmable membrane label with LEDs | Yes | Yes | No - Display |
| Vehicle Spy 3 Support | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Learn More About RAD-Comet 3 >> | Learn More About RAD-Comet 2 >> | Learn More About RAD-Meteor >> |